


Hands-On Tutorial in Mapping Information Systems
©
United Nations Children’s Fund, 1996.UNICEF GIS for Planners Hands-On Tutorial
Printed in India.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names and data used in examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise noted. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of UNICEF.
December 1996
Microsoft is a registered trademark, and Windows and FoxPro are registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States of America and other countries. Atlas GIS for Windows is a software product owned by Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc. (ESRI), USA.
CONTENTS
Lesson 1 Overview of GIS
Lesson 2 Data for Maps
Lesson 3 Tour of Atlas GIS
Lesson 4 Linking Data to a Map
Lesson 5 Saving Map Project Files
Lesson 6 Creating a Thematic Map
Lesson 7 Layout, Labeling and Annotation
Lesson 8 Printing
Frequently Asked Questions
Overview of GIS
national patterns and changes over time;
differences in outcomes within and across regions or districts.
Data for Maps
This lesson shows how to prepare data for maps. The first step is to organize the data in a spreadsheet or data base with the names and geocoded IDs for each of the indicators to be mapped. Once the data have been entered, they will be linked to a geographic file to be mapped.
You may choose to use any common spreadsheet or data base software application to enter data for maps. But to use Atlas GIS you must be able to export the data as an Excel (.xls), Lotus 1-2-3 (.wk?), text file (delimited with tabs or commas) or data base file (.dbf).
For this example, begin by entering the ID, name and infant morality rate (IMR) for each national/state/province level in South Asia as shown in the screen below. The ID for each country is derived from the international system of codification used by the United Nations. The first two digits represent the region of the world, that is, South Asia. The next three digits represent the country code. The next two digits, where they exist, represent the first sub-national level of administration (for example, state or province) It is very important that the ID is entered correctly for each data element because the data will be linked to the geographic file by this code.
|
AREA_ID |
AREA_NAME |
DATA_VALUE |
|
01050 |
Bangladesh |
123 |
|
0105001 |
Chittagong |
105 |
|
0105002 |
Dhaka |
93 |
|
0105003 |
Khulna |
83 |
|
0105004 |
Rajshahi |
89 |
|
01064 |
Bhutan |
70 |
|
01144 |
Sri Lanka |
17 |
|
01356 |
India |
79 |
|
0135601 |
Andhra Pradesh |
70 |
|
0135602 |
Arunachal Pradesh |
40 |
|
0135603 |
Assam |
89 |
|
0135604 |
Bihar |
89 |
|
0135605 |
Goa |
32 |
|
0135606 |
Gujrat |
69 |
|
0135607 |
Haryana |
73 |
|
0135608 |
Himachal Pradesh |
56 |
|
0135609 |
Karnataka |
65 |
|
0135610 |
Kerala |
24 |
|
0135611 |
Madhya Pradesh |
85 |
|
0135612 |
Maharashtra |
51 |
|
0135613 |
Manipur |
42 |
|
0135614 |
Meghalaya |
64 |
|
0135615 |
Mizoram |
15 |
|
0135616 |
Nagaland |
17 |
|
0135617 |
Orissa |
112 |
|
0135618 |
Punjab |
54 |
|
0135619 |
Rajasthan |
73 |
|
0135620 |
Sikkim |
|
|
0135621 |
Tamil Nadu |
68 |
|
0135622 |
Tripura |
76 |
|
0135623 |
Uttar Pradesh |
100 |
|
0135624 |
West Bengal |
75 |
|
0135625 |
Andaman & Nicobar Is |
|
|
0135626 |
Chandigharh |
|
|
0135627 |
Dadra & Nagar Haveli |
|
|
0135628 |
Daman & Diu |
|
|
0135629 |
Delhi |
65 |
|
0135630 |
Lakshadweep |
|
|
0135631 |
Pondicherry |
|
|
0135632 |
Jammu & Kashmir |
45 |
|
01462 |
Maldives |
34 |
|
01524 |
Nepal |
102 |
|
0152401 |
Eastern Region |
85 |
|
0152402 |
Central Region |
99 |
|
0152403 |
Western Region |
80 |
|
0152404 |
Mid-Western Region |
126 |
|
0152405 |
Far-Western Region |
124 |
|
01586 |
Pakistan |
105 |
|
0158601 |
Punjab |
104 |
|
0158602 |
Sindh |
81 |
|
0158603 |
North West Frontier Province |
80 |
|
0158604 |
Balochistan |
72 |
Once the data for the map are stored in a spreadsheet or data base file, save and close the file. It is necessary to close the data file before it can be reopened and linked to the map.
Tour of Atlas GIS
This lesson introduces you to ESRI’s Atlas GIS for Windows. It describes the main features of the system.
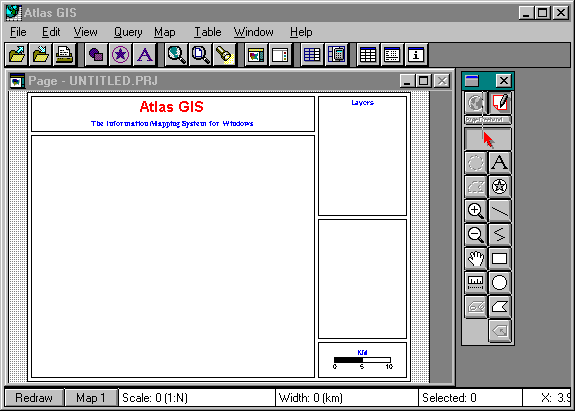
The Menu bar (at the top of the screen) displays the menu topics. As you drag the mouse across the Menu bar, each menu drops down a list of commands.
The Button bar (below the menu bar) provides short cuts to commonly used menu commands.
The Page window contains an image of the page (as it will appear in final printed form). This is the primary window, where all direct interaction with the map and page take place. The map will appear in the frame on the page along with the title, legends and other annotations.
The Tool bar (on the right side of the screen) contains buttons that you use to select and manipulate map features, text objects and other page elements.
The Status bar (at the bottom of the screen) displays the map scale, map width and number of selected map features. It also includes the Redraw button which you can click to redraw the Page window. The status bar also contains the Current Map button which you can click to change select among four possible map frames.
Menu Bar
|
File |
Perform basic file operations and program tasks, such as opening, merging, saving and printing. Also, set program preferences. |
|
Edit |
Edit map and freehand objects with standard Windows commands for copy and paste. Also, change the drawing order of objects or align selected objects. |
|
View |
Change the map and page view. |
|
Query |
Perform queries to select map features. |
|
Map |
Control the content and appearance of the map and page. Also perform advanced map operations, such as, creating buffers, combining map features and digitizing. |
|
Table |
Edit tables of data and geocodes. |
|
Window |
Open a window or arrange windows on the screen. |
|
Help |
Access the on-line help for the system which contains extensive illustrations and explanations on how to use the system. |
Button Bar
The Button bar provides shortcuts to certain menu commands. Clicking on any button is the same as choosing the command from its pull-down menu. You can use the File | Preferences command from the Menu bar to show or hide the menu bar, and to change the buttons displayed. The default Button bar shortcuts are:
|
Open |
File | Open |
|
Save |
File | Save |
|
|
File | Print |
|
Objects |
Edit | Change Properties | Objects |
|
Symbols |
Edit | Change Properties | Symbols |
|
Text |
Edit | Change Properties | Text |
|
View Map |
View | Entire Map |
|
View Page |
View | Entire Page |
|
Find |
Query | Find |
|
Layers |
Map | Layers & Themes |
|
Legends |
Map | Legends & Frames |
|
Define Col |
Table | Define Columns |
|
Calc Col |
Table | Calculate Column |
|
Table |
Window | New Table Window |
|
Stats |
Window | New Statistics Window |
|
Info |
Window | Show Info Window |
Page Window
The Page window displays an image of the page as it will appear when it is finally printed. This is the primary window where all direct interaction with the map and page takes place. It contains the map frames (maximum of 4), title, map scale and legends.
Tool Bar
|
Map/Page |
Select the map/Select the page |
|
Layers |
Select layers of the map for manipulation |
|
Circle Select/Text |
Select all features inside or touching a circle/ Add freehand text |
|
Polygon Select /Symbol |
Select all features inside or touching a polygon/ Add a symbol or point |
|
Zoom In /Line |
Zoom in on the map or page/ Add a line |
|
Zoom Out/Polyline |
Zoom out from the map or page/ Add a polyline |
|
Pan/Rectangle |
Move the map to view an area currently outside the working area/ Add a rectangle |
|
Distance/Circle |
Measure the distance between two or more points/ Add a circle |
|
Islands & Lakes/Polygon |
Combine regions into islands or lakes/ Add a polygon |
|
Reshape |
Add, delete or move vertices of map features. |
Status Bar
|
Redraw Button |
Redraws the current map and page |
|
Current Map Button |
Selects which map frame has the current focus |
|
Map Scale |
Shows the current map scale |
|
Map Width |
Shows the width of the map |
|
Selected Features |
Shows the number of map features selected |
|
Current Cursor Position |
Displays the cursor position on the map or page |
Linking Data to a Map
To link data to a map, you will create a Project directory (a subdirectory on the hard disk) where you will store all the files to create the map. There are three basic file types used by Atlas GIS to create maps: table, geographic and project files. These files store the fundamental information about your map.
Table Files -- .DBF
Data are stored in table files. These files end in the extension .DBF and are compatible with common data base management software applications, like dBASE and FoxPro. Data entered in spreadsheets can be automatically converted to table files for use with Atlas GIS.
Geographic (Geo) Files -- .AGF
Geographic information required to create maps is stored in geo files. There are several types of geo files which work together to create a map with all its features. The main file ends in the extension .AGF, and its associated files end in the following extensions: .AIF, .AGX and .AWX. Geo files are created by digitizing paper maps and are linked with GIS software packages to create maps. UNICEF ROSA has a library of geo files for all countries in South Asia.
Project Files -- .PRJ
Project files have the extension .PRJ and store the names of the .DBF and .AGF files need to create the map. It also contains information on the map’s labels and the appearance of titles, scales and legends.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1 Create a Project Directory
Create a Project directory called C:\SASIA on the hard disk. This is where you will store all the files to create the map. (See page 29 for detailed instructions on creating directories.)
Copy the spreadsheet file IMR.xls or data base file IMR.dbf (created in Lesson 2) to the Project directory . If you are using a spreadsheet file, it will be converted automatically by Atlas GIS to a data base file, .DBF, which will subsequently be linked to the geo files to create a map. (See page 29 for detailed instructions on copying files.)
Copy the geo files of the countries of South Asia to the Project directory. The files you need are:
Atlas_01a.agf, Atlas_01a.agx, Atlas_01a.aif, Atlas_01a.awx, Atlas_01a.lay
K_lg.agf, K_lg.agx, K_lg.aif, K_lg.awx, K_lg.lay
Step 2 Start Atlas GIS
Start the application. Each time you start it, a default project file (called DEFAULT.PRJ) is automatically opened. This project file contains the default page settings.
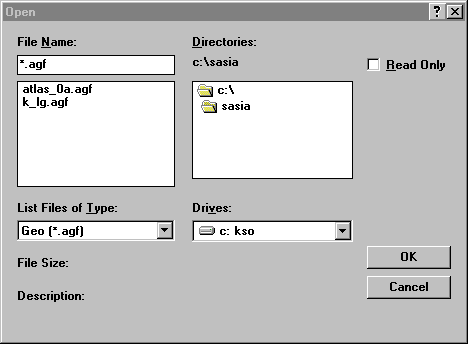
Step 3 Open the Geo File of South Asia
Click File | Open on the Menu bar to display the Open dialog box. Select Geo (*.agf) from the List Files of Type drop-down list. Click on the Geo file named Atlas_0a.agf. Click OK. Repeat the process to open the Geo file named K_lg.agf.
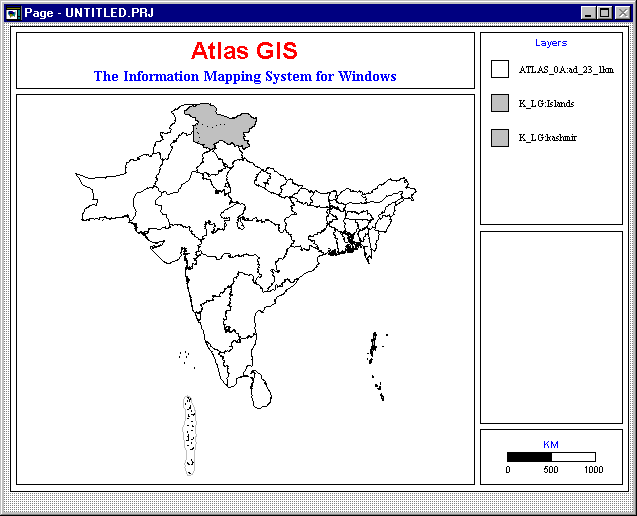
The following map of South Asia will appear.
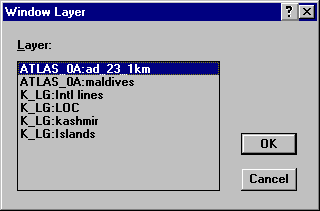
Click Window | New Table Window… from the Menu bar to display the following dialog box. Then click OK.
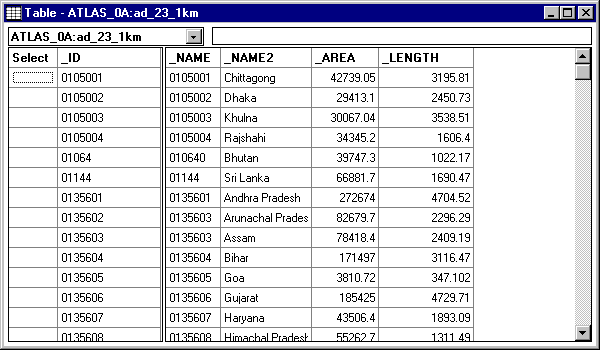
The following table will be displayed showing the contents of the geo files.
Close this table window before going on.
Step 4 Open and Link the Data File
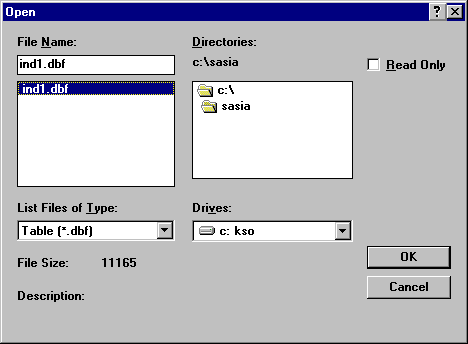
Click File | Open from the Menu bar to display the Open dialog box again. This time select Table (*.dbf) or Excel (*.xls) from the List Files of Type drop-down list. Click on the file named IMR.dbf or IMR.xls and click OK.
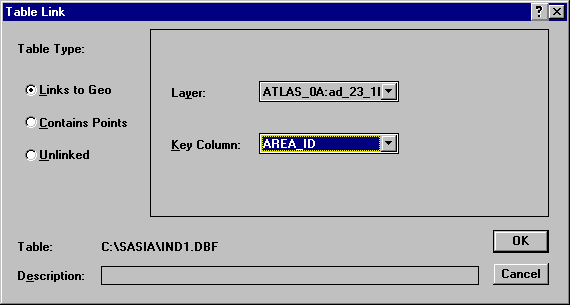
Change the Table Type to Links to Geo. Change the Layer to Atlas_0a. Change the Key Column to Area_ID. Click OK to link the table of data to the map.

Click Window | New Table Window… from the Menu bar to display the Window Layer dialog box again. Then click OK.
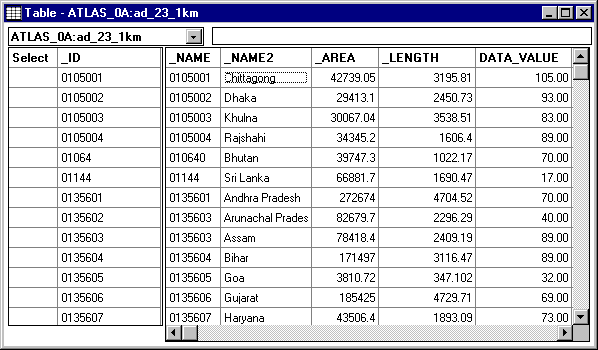
The following table will be displayed showing the contents of the geo file again plus new columns of data linked from the data base. Note that Data_value contains the IMR data.
Close the Table window before going on.
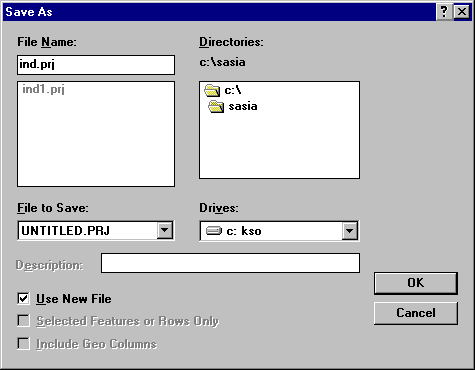
Saving Map Project Files
To save the work that you have done so far, click File | Save As… on the Menu bar to display the Save As dialog box. Enter IND1.PRJ as the File Name. Click OK to save the project file.
Creating a Thematic Map
Now that the data are linked to the map, it is possible to create a thematic map. A thematic map represents data by applying shading, color-coding, or dots in the regions of the map. Atlas GIS provides tools to create three types of thematic maps. Ranged maps show data divided into distinct ranges. Each data range is represented by a color, fill pattern, line style or symbol type. Proportional maps depict data by varying the percentage of fill, line width or symbol size for each feature of the map in direct proportion to its data value. Dot-density maps show regions filled with dots that are randomly placed and uniformly sized. The number of dots in a region is proportional to its data value.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1 Select Layers & Themes
To create a range filled map of South Asia based on IMR, click Map | Layers & Themes on the Menu bar to display the Layers & Themes dialog box. Note that there are several layers shown, but some layers are turned on while others are off ( ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ appears immediately after the Layer Name under the Layer On column). Select the Atlas_0a_23_1 layer for a theme by clicking the Layer name. Be sure that this layer is turned on by ensuring that the word ‘Yes’ appears under the ‘Layer On’ column immediately after the Layer Name. If the word ‘No’ appears, click it to change it to ‘Yes.’
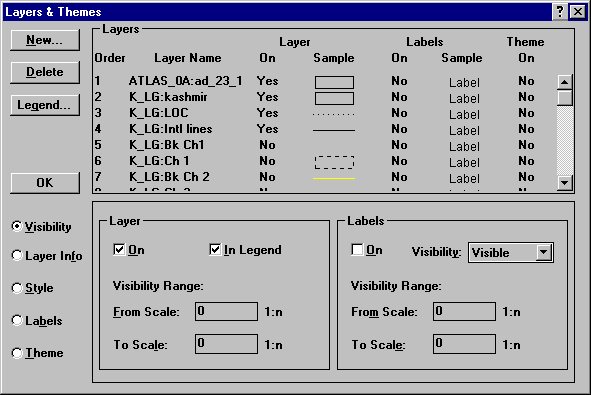
Step 2 Enter an Expression
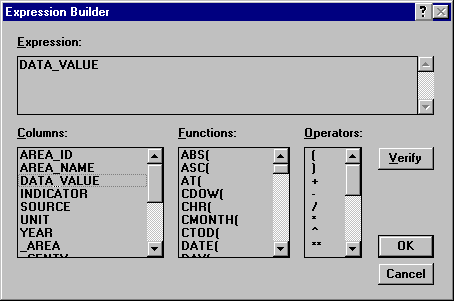
Click the Theme option button to change the lower subpanel to display the theme information for the selected layer. In the Theme subpanel, click the Theme On check box. Then, in the Variable 1 group box, click on the Expression […] button to display the Expression Builder.
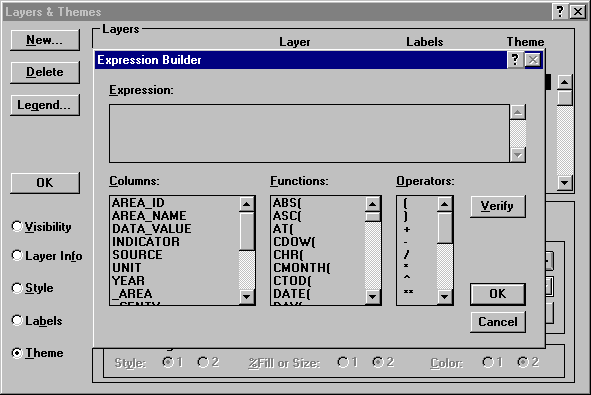
Double click on DATA_VALUE in the Columns list to select this value as the value of the IMR for each region. Click OK to return to the Layers & Themes dialog box.
Step 3 Specify the Theme Settings
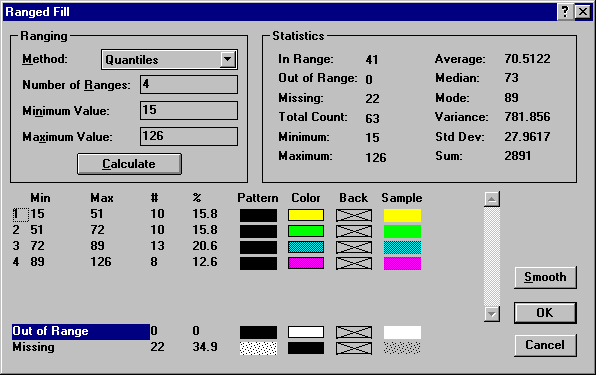
In the Variable 1 group box, choose Ranged Fill in the Map Type list box. Click the Ranges… button to display the Ranged Fill dialog box.
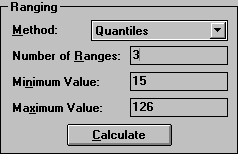
In the Ranging box, click the Method list to display the various options for determining ranges. Choose Quantiles from the Method list. Change the Number of Ranges to 3. Press the Calculate button to update the ranges that will be depicted in the map.
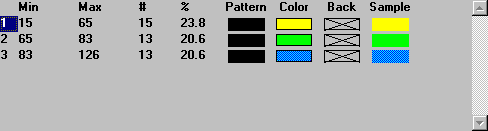
Notice that the bottom half of the dialog box now has three ranges as show below.
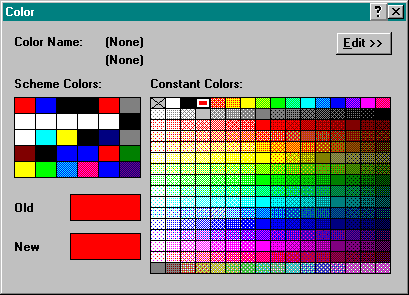
Click on the Color swatch of one of the ranges to display the Color dialog box. Click on a Constant color to change the color for the selected range. Change the colors of the ranges to yellow, orange and red. Click OK to return to the Layers & Themes dialog box.
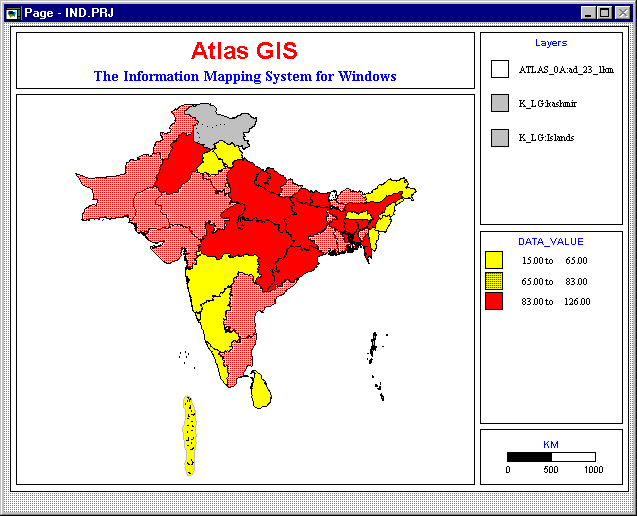
Click OK on the Layers & Themes dialog box to view the thematic map below.

Step 4 Customize the Theme Legend
To customize the theme legend, right click on it to display the Theme Legend - Ranged dialog box. In the Legend box, change the Title to ‘IMR.’
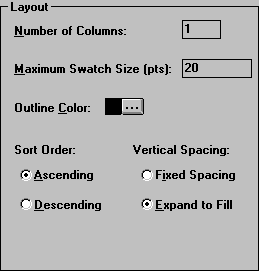
In the Layout box, click the Vertical Spacing: Expand to Fill option.
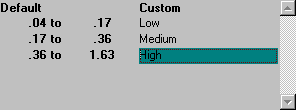
In the Descriptions box, click the Custom option. Then enter custom labels for the three ranges as, Low, Medium and High. Then click OK to return to the map.
Step 5 Customize the Map Title
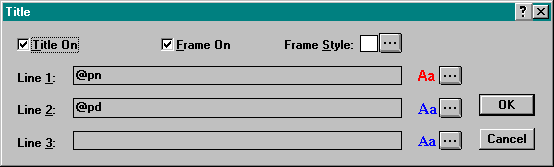
Right click the title box on the map to display the Title dialog box. Change the Line 1 of the title to "INFANT MORTALITY RATE" and Line 2 to "SOUTH ASIA." Then click OK to return to the map.
Step 6 Save the Project File
Click File | Save from the Menu Bar to save the work that you have done this far to IND1.PRJ project file.
Layout, Labeling and Annotation
The thematic map that you prepared in the previous lesson can be enhanced with improved layer settings, labels, arrangement of page elements and resized page frames.
Adding and Changing Layer Settings
Layers allow you to graphically depict different kinds of features.
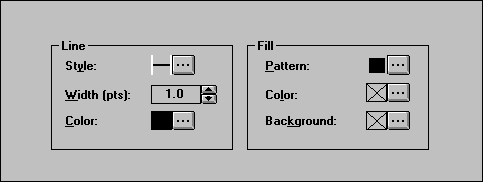
Right click anywhere in the map frame to display the Layers & Themes dialog box. Select any layer and turn it on (‘Yes’ immediately after the Layer Name). Click the Style option (on the lower left side of the screen). The lower subpanel changes to display Line and Fill boxes. Change the Line Style or Fill Color for the layer selected.
Adding Labels
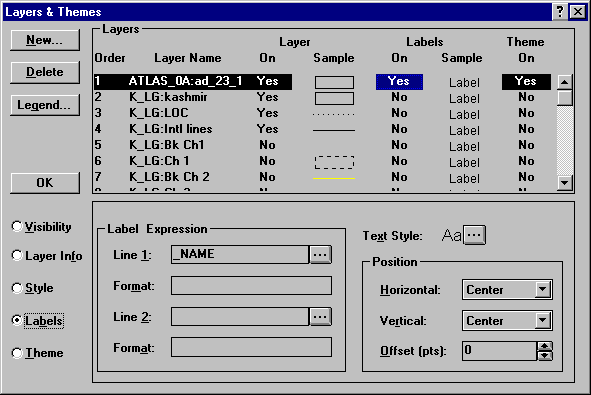
Right click anywhere in the map frame to display the Layers & Themes dialog box. In the Layers box, toggle the Labels On column setting for the layer Atlas_0a_23_1 to ‘Yes.’ Then click the Labels option button on the lower left side of the dialog box. Notice that the subpanel changes to display the label options for the layer. In the Label Expression group box, Line 1 displays the expression for the first line of the label. You can have two-line labels, such as the name of the map feature in the first line and the value of an indicator in the second line.
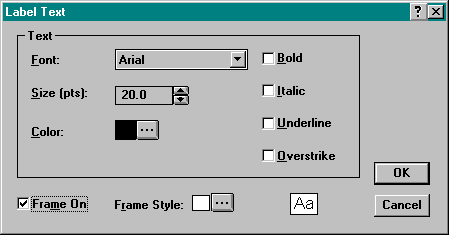
Click on the Text Style button to change the font used for the label or to create a frame around the label.
Click OK to view the map with labels.
Changing and Arranging Page Elements
You can change the layout of the page by choosing Map | Legends & Frames from the Menu bar to display the Legends & Frames dialog box. In this box, toggle map frames, map legends and theme legends on or off.
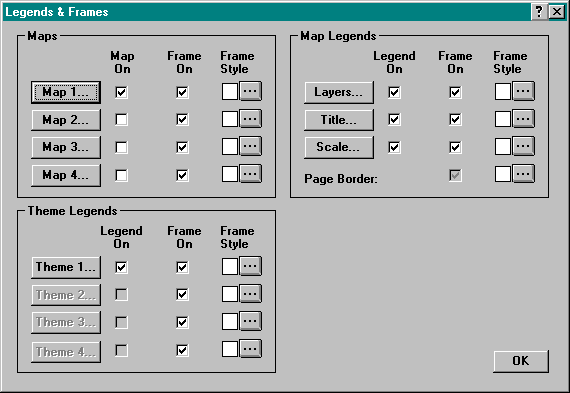
Resizing Page Frames
Click on the Page button of the Tool bar to work with page frames. Click on the Title frame to select it. Notice that edit handles appear on the frame around the title. Drag the edit handle on the right side of the frame to increase the width of the Title frame. Click on the Map frame to resize it. Click on the theme and layer legend boxes to resize them.
Printing
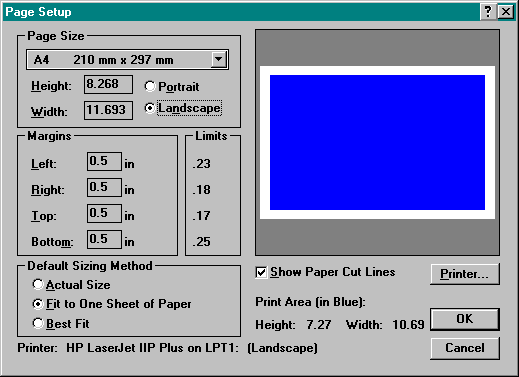
Click File | Page Setup… on the Menu bar to specify the page size, margins and default sizing method for the page which will contain the final printed map.
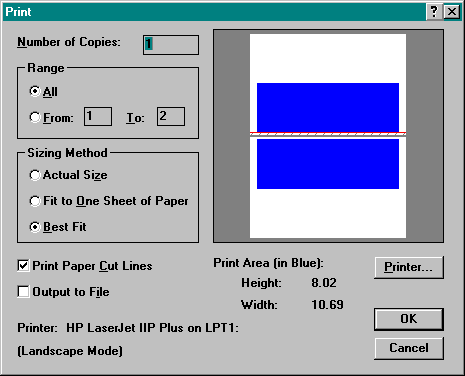
Click File | Print… to display the Print dialog box to specify the number of copies to print and the Sizing Method. The Sizing Method has been set to Best Fit in this example. The map will be printed on two pages as shown in the blue and white box on the right side of the screen. To print the map on one page, select Fit to One Sheet of Paper. This will reduce the size of the map to dimensions of one sheet of paper. Select Actual Size to print the map at the same size as the page size. This may result in the map printing on one page, if the dimensions are smaller than the paper or tiled on several pages if the dimensions of the map are larger than one piece of paper. Click OK to send the map to the printer specified.
Advanced GIS Features
This hands-on tutorial introduces the basic features of Atlas GIS. There are many advanced features which are explained in the Atlas GIS User’s Guide and the Atlas GIS Reference Guide. These features include:
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I create a Project Directory?
Method using MS Windows 3.x:
Step 1 Double-click the File Manager icon to start the application.
Step 2 Click the C:\ directory symbol at the top of the directory tree
in the left pane of the C:\*.* window.
Step 3 Click File | Create Directory… from the main menu to display
the Create Directory dialog box.
Step 4 Center the new directory name SASIA in the slot provided
in the Create Directory dialog box. Click OK.
Step 5 Click File | Exit from the main menu to exit.
Method using MS DOS:
Step 1 At the C: prompt, type the Make Directory command:
MD ASIA [Enter]
2. How do I copy files to the Project Directory?
Step 1 Double click the File Manager icon to start the application and
to display one window.
Step 2 Click Window | New Window from the main menu to open a
second window.
Step 3 Click Window | Tile to arrange the two windows neatly in the space
available on the screen, one above the other.
Step 4 Click the C:\SASIA directory in the left pane of the upper window.
Step 5 Insert the floppy with files to be copied into Drive A.
Step 6 Click the Drive A icon at the upper left corner of the lower window.
The window will now display the directory of files on the floppy diskette.
Step 7 To copy a file from the floppy diskette to C:\SASIA, click and drag
the name of the file on the floppy (in the lower right window pane) to the
right window pane of the C:\SASIA window at the top of the screen.
"Click and drag" means to position the mouse over the name of the file,
then, hold the left mouse button down while moving the mouse to
the position on the screen where you want to move the file name.
Release the mouse button when you have reached the place on the
screen where you want to move the file.
3. Using Atlas GIS, how do I make a box (or frame) around a map label.
Step 1 Click Map | Layers and themes from the Main menu.
Step 2 Click the Layer Name of the layer of labels you wish to change.
Step 3 Click the Labels button on the lower left side of the window.
Step 4 Click the Text Style button on the right side of the window.
Step 5 Click the Frame On box to make a box around each label.
Step 6 Click the Frame Style button to adjust the appearance of the
line, fill, corners and shadow of the label frame, if desired.
4. Using Atlas GIS, how do I create a map showing two variables, one as a ranged fill and the other as a proportional symbol?
Step 1 Although it is possible to create a theme based on two variables, related to
to one layer, you must then select one of the two as the controlling variable.
When the two variables that you want to display are independent, one
solution is to create two layers for the same geographic areas and then create
one theme for each of the layers.
To begin this process, click Query | Select by Layer… to select the layer that
you want to depict with two variables. Click the name of the layer that you want
in the Select by Layer dialog box, then click OK to return to the main screen.
The features of the layer you have selected will be highlighted now.
Step 2 Click Edit | Copy to Layer… to display the Copy to Layer dialog box.
Step 3 Select the name of the layer to copy features from.
Step 4 Click the Selected Features Only box.
Step 5 Click the New Layer… button.
Step 6 Enter the name of the new layer and a description. Click OK.
Step 7 Click OK to create the new layer and to copy the features to it.
Step 8 Click Map | Layers and Themes… to display the Layers and Themes dialog box.
Step 9 Create a ranged fill theme based on one variable for one of the two layers.
Step 10 Create a proportional symbol theme based on another variable
for the other layer. Note that it is possible to change the drawing
order of the layers by clicking and dragging the number of the layer
up or down the list of layer names. It is important that the ranged fill
layer be drawn first, then the symbol layer, otherwise the symbols will
be painted over by the ranged fill.
5. Using Atlas GIS, how do I change miles to kilometres in the map scale.
Step 1 Click File | Preferences from the main menu.
Step 2 Click the Units button on the left of the windows.
Step 3 Change Map Distances from miles to kilometres, and
change other units, if desired.
for some reason they are not showing. Why?
Step 1 Click File | Preferences from the main menu.
Step 2 Click the Workspace button on the left of the windows.
Step 3 Change Minimum Label Size to the size of the smallest
label size. Click OK.
7. How do I copy a map directly from Atlas GIS into a word processing document?
Step 1 Click the Map button at the top left corner of the Tool Bar.
Step 2 Click Edit | Copy Visible Page.
Step 3 Activate the word processing document and place the
the cursor where you want to insert the map.
Step 4 Click Edit | Paste from the word processor’s main menu.