Conventional ECC design approach is constructed on the paradigm of the relationships between microstructures, processing, material properties, and performance. In this project, emphasis is placed on the incorporation of sustainability consideration into ECC design regimen, specifically, the feasibility of reducing high cement usage in ECC mix by substitutions of fly ash and bottom ash. The mix design is guided by micromechanics models that link the critical parameters of fiber/matrix interface properties and matrix toughness to composite ductility. Material sustainability indicators are adopted to assess the material sustainability performance.
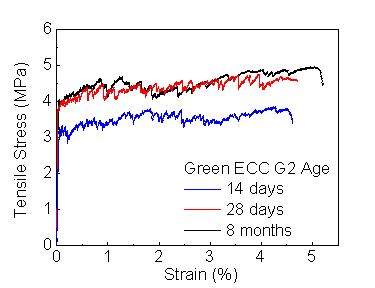
The resulting green ECC demonstrates that, when properly tailored, high strain capacity is retainable in the presence of high volume of low quality by-products. The resulting composites demonstrated robust tensile strain capacity at 3-4% and tensile strength above 4.5 MPa while material sustainability indices were significantly improved (Fig. 1).
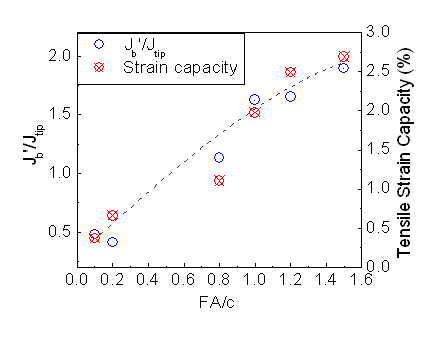
The micromechanics parameter study revealed the general descending trend of interface frictional stress and chemical bond with increase of fly ash content, which in turn modify the PVA fiber bridging behavior resulting in higher complementary energy Jb’ values. In addition, increase of fly ash content also leads to a lowering of the matrix toughness Jtip. Both trends are favorable to strain-hardening. Strong correlation between Jb’/Jtip and strain capacity was observed which further support this ratio as a good indicator of composite strain-hardening potential (Fig. 2).
The design process demonstrated that sacrifice of high material performance was not inevitable when using low quality substitutions or wastes, as long as the governing micromechanics parameters were carefully tailored. Although this study focused on tensile ductility of cementitious composites, the authors believe that this approach is broadly applicable to other sustainable material design practice. |