References (aka Mario's
Special Friends!)
![]() Doyle, M. P.; Dorrow, R. L.; Tamblyn, W. H.; Buhro, W. E. Tetrahedron Lett . 1982 , 23 , 2261-2264.
Doyle, M. P.; Dorrow, R. L.; Tamblyn, W. H.; Buhro, W. E. Tetrahedron Lett . 1982 , 23 , 2261-2264.
The focus of this article was on the regioselectivity of cyclopropanation between conjugated, mono-substituted dienes and with ethyl diazoacetate that are catalyzed by transition metal complexes. It showed that the reaction occurred at the un-substituted carbon in nearly all of the trials with various dienes. The Rh 2 (OAc) 4 complex gave the greatest regioselectivity and cyclopropane yields over the other catalysts: Rh 6 (CO) 16 , CuCl P(O- i -Pr) 3, and PdCl 2 2PhCN. Doyle et. al report that since Rh 2 (OAc) 4 promotes the greatest yield and regioselectivity, this catalyst was used as a reference point to measure metal carbene selectivity with the other three catalysts.
Reference 1:
![]() Miller, A. M.; Wiechang, J.; Nguyen, S. T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Eng. 2002 , 41 , 2953-2956.
Miller, A. M.; Wiechang, J.; Nguyen, S. T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Eng. 2002 , 41 , 2953-2956.
Miller et. al discuss rhodium propanation reactions that do not exhibit high selectivity unless the reaction is intramolecular. The authors also cite another article by Doyle (Doyle, M. P.; Bagheri, V.; Wandless, T. J.; Harn, N. K.; Brinker, D. B.; Eagle, C. T.; Loh, K. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990 , 112 , 1906-1912.) However, Miller et. al focus particularly on ruthenium complexes to catalyze olefin (alkene) cycloproponation, which is similar to our mechanism. Significant to this study was the finding that smaller molecules, such as ethyl diazoacetate, which was used by Doyle (1982) has lower selectivity than larger molecules like tert -butyl diazoacetate. The authors cite Doyle's paper when they mention how a - b unsaturated carbonyl compounds and nitriles can yield racemic cyclopropanes.
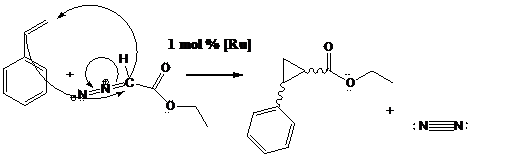
The alkene is mono-substituted, which is one of Doyle's greatest points of his paper. Even though the catalysts are different, they are both transition metal elements which is the key feature for such catalysts. In the above reaction, a stereoisomeric mixture, but a considerably greater amount of the trans isomers are formed.
Reference 2:
![]() Jan, D.; Simal, F.; Demonceau, A.; Noels, A. F.; Rufanov, K. A.; Ustynyuk, N. A.; Gourevitch, D. N. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999 , 40 , 5695-5699.
Jan, D.; Simal, F.; Demonceau, A.; Noels, A. F.; Rufanov, K. A.; Ustynyuk, N. A.; Gourevitch, D. N. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999 , 40 , 5695-5699.
These authors moved away from the typical rhodium and ruthenium complexes, and instead studied the ability of chromium complexes in catalysis of olefin cyclopropanation. They reference Doyle's paper in the introduction when they discuss how ethyl diazoacetate and an a - b unsaturated carbonyl compound form cyclopropanes and vinyl C-H insertion products. The main catalyst they use is the bis(imido) chromium (VI). The same reaction scheme from Doyle, our own article, and that of reference 1 occurred. The chromium complex catalyzed the concerted mechanism in which N 2 gas is lost from the molecule and a cyclopropane ring forms, with the reaction occurring at the less-substituted site of the mono-substituted alkene.
Thanks to Luigi, Yoshi, Toadstool, and the whole gang! The Princess's prognosis is lookin' good! Now it's up to the Power Rangers to finish
The Synthesis of (-)-Spirotryprostatin B!!!
References used for this Project
1 Marti, C.; Carreira, E.M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005 , 127 , 11505-11515.
2 http://www.pump114.co.kr/KDS210C.HTML
3 http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Celite
4 http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/ALDRICH/401765
5 http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/organic/orglab/tech/oilBath.htm
6 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_thiosulfate
7 Doyle, M.P.; Griffin, J.H.; Bagheri, V.; Dorow, R.L. Organometallics , 1984 , 3 , 53-61.
