H-NMR Correlation
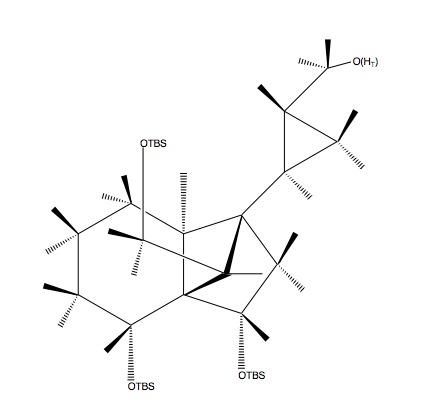
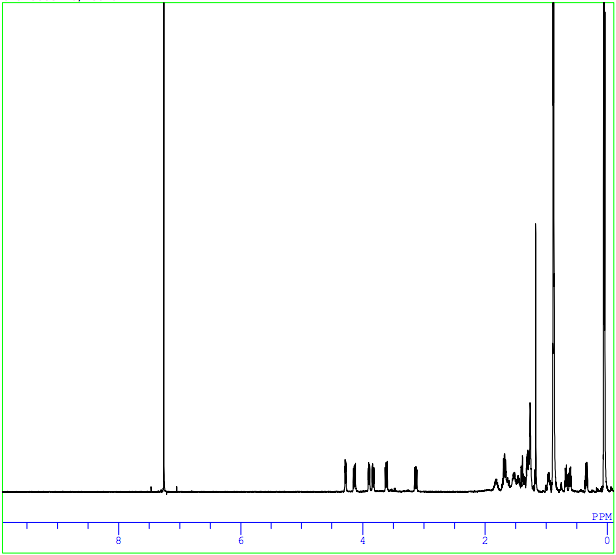
Congratulations! After a journey through Candyland, you understand every aspect of the experiment and have made it to Candy Castle! Now you can use your 215H expertise to help King Kandy analyze his 1H-NMR data!
| Assignment | Shift | Integration | Splitting Pattern | J-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
HA |
1.01-0.93 |
1H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HB |
0.63-0.59 |
1H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HC |
0.70-0.66 |
1H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HD |
0.37-0.32 |
1H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HE/HJ |
1.41-1.35 |
2H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HF/HK |
1.73-1.61 |
2H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HG |
4.29 |
1H |
Doublet of Doublets |
7.4 Hz, 2.3 Hz |
HH |
1.86-1.79 |
1H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HI |
3.90 |
1H |
Doublet of Doublets |
8.5 Hz, 3.8 Hz |
HL/HN |
1.55-1.43 |
2H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HM/HO |
1.32-1.26 |
2H |
Multiplet |
n/a |
HP |
3.83 |
1H |
Doublet of Doublets |
10.6 Hz, 4.0 Hz |
HQ |
4.14 |
1H |
Doublet of Doublets |
10.6 Hz, 6.6 Hz |
HR |
1.17 |
3H |
Singlet |
n/a |
HS1 |
3.62 |
1H |
Doublet of Doublets |
10.9 Hz, 5.7 Hz |
HS2 |
3.14 |
1H |
Doublet of Doublets |
10.9 Hz, 8.6 Hz |
HT |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
OTBS |
0.89, 0.88, 0.88, 0.06, 0.06, 0.05, 0.04 |
9H, 9H, 9H, 6H, 3H, 6H, 3H |
All Singlets |
n/a |
Explanation
HA: The 13th peak at 1.01-0.93 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom pointing up off the cyclopropane ring, adjacent to the CH2OH group. It is slightly deshielded from the OH nearby and the stress of the cyclopropane ring. It is split by 4 adjacent hydrogen atoms.
HB: The 18th peak at 0.63-0.59 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom pointing down off the bottom left corner of the cyclopropane group. It is shielded by the sp3 carbon atom it is bound to. It is split by the 3 adjacent hydrogen atoms.
HC: The 17th peak at 0.70-0.66 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom pointing up at the tip of the cyclopropane ring. It is shielded by the sp3 carbon atom it is bound to. It is split by its two bond neighbor and two three bond neighbors.
HD: The 19th peak at 0.37-0.32 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom pointing down at the tip of the cyclopropane ring. It is shielded by the sp3 carbon atom that it is bound to. It is split the same as the above hydrogen.
HE/HJ: The tenth peak at 1.41-1.35 ppm corresponds to the two hydrogen atoms pointing up on the carbons adjacent to both lower OTBS groups. They are shielded by the sp3 carbon atoms they are bound to, and they are split by their many adjacent neighbors.
HF/HK: The eighth peak at 1.73-1.61 ppm corresponds to the two hydrogen atoms pointing down on the same carbons as the above hydrogens. They are shielded by the carbon atoms they are bound to, but are slightly deshielded by the adjacent OTBS groups. They are split by their many neighbors.
HG: The first peak at 4.29 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom on the same carbon as the OTBS group on the cyclopentane. It is deshielded by the inductive effect of the OTBS group and the carbon bridge above it. It is split by its two adjacent neighbors.
HH: The seventh peak at 1.86-1.79 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom attached to the carbon bridge on the cyclopentane ring. It is slightly deshielded due to the ring strain, and is split by two neighbors.
HI: The third peak at 3.90 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom attached to the carbon with the OTBS group on the cyclohexane ring. It is deshielded by the inductive effect of the OTBS group and the carbon chain above it. It is split by two neighbors.
HL/HN: The ninth peak at 1.55-1.43 ppm corresponds to the two hydrogen atoms pointing up on the top left of the cyclohexane ring. They are deshielded by the inductive effect of the OTBS group above them. They are split by their many neighbors.
HM/HO: The 11th peak at 1.32-1.26 ppm corresponds to the two hydrogen atoms pointing down on the same carbons as the above hydrogens. They are shielded by the carbon atoms they are bonded to, and could be deshielded by the inductive effect of the OTBS group above the ring.
HP: The fourth peak at 3.83 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom pointing up on the carbon chain above the cyclohexane ring. It is deshielded by the inductive effect of the adjacent OTBS group. It is split by its two neighbors.
HQ: The second peak at 4.14 ppm corresponds to the hydrogen atom pointing down on the same carbon as above. It is deshielded by the inductive effect of the adjacent OTBS group and the ring below it. It is split by two neighbors.
HR: The 12th peak at 1.17 ppm corresponds to the 3 hydrogen atoms of the only methyl group in the molecule. They are shielded by the carbon atom they are bound to, and have no neighbors so the peak is a singlet.
HS1: The fifth peak at 3.62 ppm corresponds to one of the two hydrogens of the CH2 group bonded to the OH. The hydrogen atom is deshielded by the inductive effect of the adjacent alcohol. It is split by its two neighbors.
HS2: The sixth peak at 3.14 ppm corresponds to the the other hydrogen in the same place as the one above. It is also deshielded by the inductive effect of the adjacent alcohol, and is split by two neighbors.
HT: This hydrogen atom is the hydrogen of the OH group, but it was not listed by the authors as a peak on the spectrum.
OTBS: The peaks for OTBS show up at 0.89, 0.88, 0.88, 0.06, 0.06, 0.05, and 0.04 ppm. They are shielded by the carbon atoms they are bound to and the silicon atom that is less electronegative than carbon.
