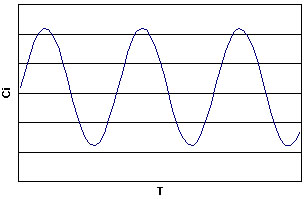

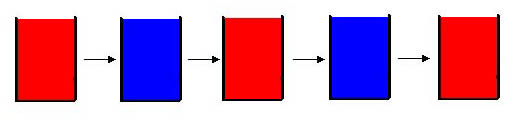
The Belousov-Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction is a chemical oscillatory reaction, fluctuating in color. Named after B. P. Belousov (who discovered the reaction) and A. M. Zhabotinsky (who continued Belousovīs early work), the reaction originally consisted of a one-electron redox catalyst, an organic substrate that is easily brominated and oxidized, and a bromate ion in form of NaBrO3 or KBrO3 all dissolved in sulfuric or nitric acid. The typical catalyst that is used is ferroin. Ferroin, in its oxidized state, has a blue color, while in its reduced state ferroin is red. As the BZ reaction alternates between the oxidized state and reduced state, the solution changes its color.