Additional Homework Problems
P12-28B
The formation of styrene from vinylacetylene is essentially irreversible and follows an elementary rate law:
2 vinylacetylene 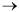 styrene
styrene
2A 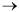 B
B
- Determine the conversion achieved in a 10 dm3 PFR for an entering temperature of 675 K. Plot the temperature and conversion down the length (volume) of the reactor.
- Vary the entering temperature and plot the conversion as a function of entering temperature
- Vary the ambient temperature in the heat exchanger and find the maximum ambient temperature at which runaway will not occur in the reactor.
- Compare your answers with the case when the reaction is carried out adiabatically.
- Repeat part B assuming that the reaction is reversible, KC = 100,000 at 675 K. In addition, a stream of inerts (CP1 = 100 J/(mol °C)), with FI = 3 FA0, enters the reactor. Plot the conversion as a function of the entering temperature. Is there a maximum? If so, why? If not, why not?
- Ask another question or suggest another calculation that can be made for this problem.
Additional Information
CA0 = 1 mol/dm3
Ua = 5 kJ/(s dm3)/K
FAo = 5 mol/s
Ta = 700 K
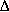 HRX = -231 - 0.012(T - 298) kJ/mol
HRX = -231 - 0.012(T - 298) kJ/mol
CPA = 0.12222 kJ/(mol K)
k = 1.48 * 1011 exp(-19124/T) dm3/(mol s)
T0 = 675 K
[3rd Ed. P8-9]
![]() styrene
styrene ![]() B
B
![]() HRX = -231 - 0.012(T - 298) kJ/mol
HRX = -231 - 0.012(T - 298) kJ/mol