![]()
|
|
Type 7 Home Problem -- Solution
Problems where the student must explore the situation by varying operating conditions
or parameters.
We will use the Homogeneous Example 4 Solution as the basis for our solution here, so consult that page for a more extensive derivation. Some of the equations and values will need to be revised for the present situation.
We have a new differential equation for B:
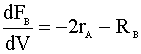
We need to insert our new rate law:
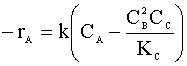
Finally, we will need new values for the volumetric flow rate (vo):
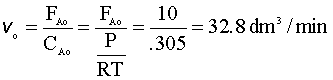
Below are the simultaneous differential equations, as entered in Polymath:
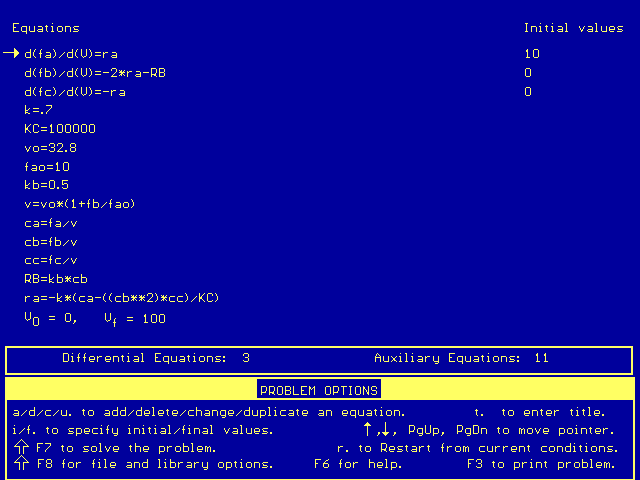
The conversion under these conditions is: X = 0.73
When k = 2, kB = 10, and KC = 107 (their largest values), the conversion is greatest:

X = 0.997
These results make sense. As KC increases, the second term in our rate law (the one that represents the reverse reaction) decreases, so more product will be formed and the conversion will increase. As k increases, the reaction rate will increase, again causing more product to form and the conversion to increase. As kB increases (remember that kB represents how quickly product B can pass through the membrane), the concentration of B in the reactor decreases, which drives the reaction towards the products. Once again, the conversion will increase.
A plot of conversion versus the product of our constants (KC*kB*k) is shown below. In each case, two of the constants are maintained at their original value, while the third is varied. Under the given conditions, changes in the equilibrium constant (KC) have almost no effect on the conversion, but the conversion varies strongly with changes in our rate constant (k).
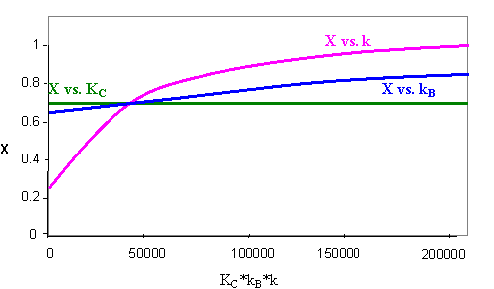
The fact that the equilibrium constant (KC) has almost no effect on the conversion means that this reaction is essentially irreversible. This reaction could be carried out in a PFR with the same effectiveness. This is only true for our higher range of KC.
The following graph displays the difference in conversion between a PFR and our membrane reactor over a lower range of equilibrium constants:
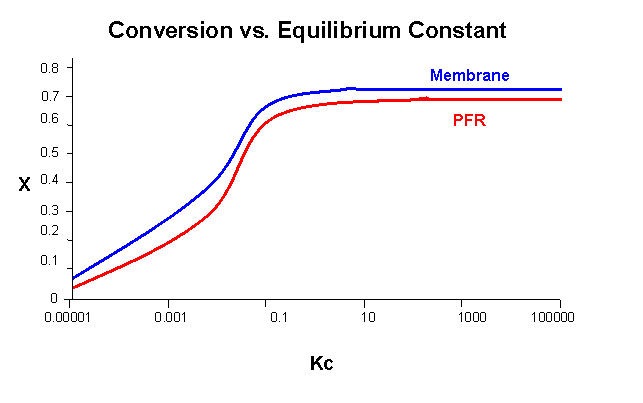
Although the difference in conversion looks nearly constant, the percent difference in conversion (see the graph below) increases significantly at lower KC values.
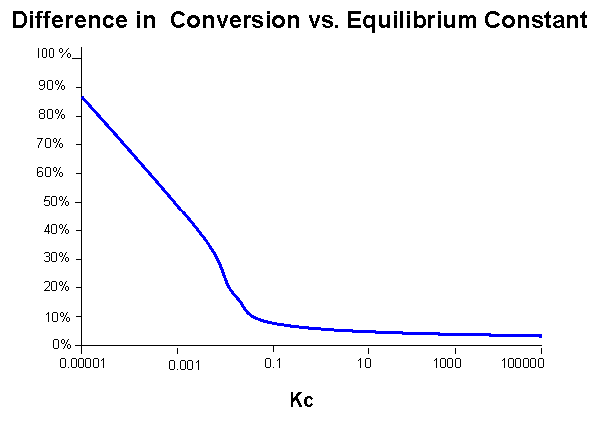
From this information, we conclude that the membrane reactor is most effective (in comparison to other reactors) when the reaction does not favor the products.
![]() Back to Homogeneous Example 7
Back to Homogeneous Example 7
CRE Thoughts Ten Types Homogeneous Example 7