Development of Two Photon NSOM
In studies of extended samples, the super resolution of NSOM
is ultimately lost due to fluorescence generated outside of the high resolution
region near the probe aperture. Furthermore, photobleaching and collateral
photochemical damage of the sample due to excitation light far from the
probe can create additional problems, especially in biological experiments
requiring UV photo-excitation.
As has been demonstrated in confocal microscopy, the use
of two-photon excitation greatly reduces the excitation volume due to its
quadratic dependence on light intensity. Limiting the excitation
to a small volume near the aperture (i.e. the region of greatest intensity)
will reduce the total number of molecules excited away from the probe,
leading to reduced rates for photochemical damage and improved resolution
in images of extended samples.
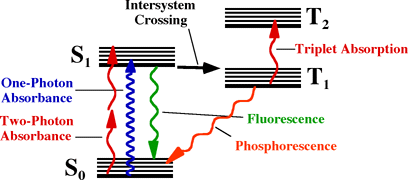
Figure 7. Jablonski diagram showing one and two-photon absorption.
Two Photon Image

