 The West County Toxics Coalition
The West County Toxics Coalition
One of the worst industrial offenders is Chevron. The oil company operates a refinery and other industrial facilities in Richmond, California. Chevron stores over 11 million pounds of toxic, explosive, and corrosive chemicals at this refinery, often very close to large population centers. When it accidentally releases these chemicals into the environment, Chevron endangers the lives of the local community members.
In fact, Chevron had 304 accidents between 1989 and 1995 -- major fires, spills, leaks, explosions, toxic gas releases, flaring, and air contamination. The people of Richmond are subject to severe injuries and illnesses. As Henry Clark, leader of the West County Toxics Coalition, reported after a toxic release in 1992, "There's stuff here that's deadlier than (in) Bhopal." (Bhopal was the site of the Union Carbide chemical leak in 1984 that killed 2,000 people and injured 20,000 more.) Richmond was an area waiting to explode.
Back to Table of ContentsIn 1993, Chevron made plans to increase its chemical storage and the number of hazardous chemicals in the Richmond area. It claimed that it was just trying to comply with the mandates of the Clean Air Act. In the company's opinion, it was all part of the process of developing a cleaner burning gas to stop the air pollution problem in the San Francisco Bay Area. Unfortunately these changes were going to pose increased risks to the local community. This community was mostly poor and mostly African American. It was a clear case of environmental injustice.
The stage was set for a confrontation. The local citizens were going to battle for their lives -- for their health, for their safety, and for the future of their town.
Back to Table of Contents The West County Toxics Coalition
The West County Toxics Coalition
 Communities for a Better Environment (CBE)
Communities for a Better Environment (CBE)
 Golden Gate University Environmental Law and Justice
Clinic
Golden Gate University Environmental Law and Justice
Clinic
 Chevron
ChevronOne of the largest oil companies in the world, Chevron operates refineries and industrial plants in Richmond, California, in close proximity to a poor, African-American community. Chevron is a large multinational corporation, with profits in the billions of dollars. Chevron is also one of the wealthiest companies in the world -- a member of the Fortune 500. The company has spent millions of its dollars on a populist advertising campaign to promote its concern for environmental issues. "Do people care about the environment?" Chevron asks in its ads. Then it answers its own rhetorical question: "People do." (Community groups have responded with protest signs that say "Do people destroy the environment? People do.")
Back to Table of ContentsRichmond, California is located on the San Francisco Bay, just across the Richmond-San Rafael Bridge from wealthy Marin County. However, Richmond itself is anything but wealthy. The community that lives within the zip code 94801 is one of the poorest in the state. According to the 1990 United States census, 44.2 percent of all Richmond children under 18 years of age live in poverty. Not coincidentally, this is the same zip code in which Chevron owns and operates its refinery. The red pin below shows the location both of this community and of the Chevron facilities.
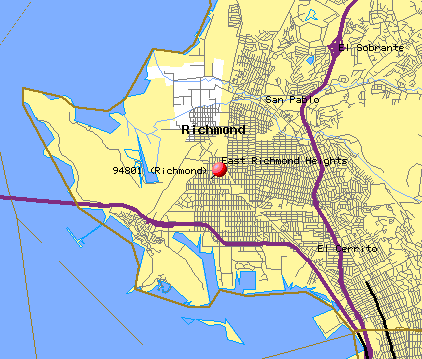
The Richmond community (zip code 94801) is mostly made up of African Americans and other ethnic groups, as the following table indicates:
Ethnic Composition of Richmond, California
| Ethnic Group |
Total Population in Richmond Zip Code 94801 |
Percentage of Total Population |
| White |
6435 |
26.9% |
| African American |
11672 |
48.8% |
| Native American, Eskimo, or Aleut |
182 |
0.8% |
| Asian or Pacific Islander |
1956 |
8.2% |
| Other |
3659 |
15.3% |
The education level of the Richmond community (zip code 94801) is also very low, as the following chart demonstrates.
Educational Attainment of Richmond Adults (age 25 and above) in zip code 94801
| Education level attained |
Total number of Richmond adults over 25 years of age who have attained this level of education (All races) |
Percentage of total adult population over 25 years of age in Richmond |
| Less than 9th grade |
2481 |
18.0% |
| 9-12th grade, no diploma |
2819 |
20.4% |
| High school degree (or equivalent) |
3170 |
22.9% |
| Some college, no degree |
2751 |
19.9% |
| Associate degree |
783 |
5.7% |
| Bachelor's degree |
1158 |
8.4% |
| Graduate or professional school |
657 |
4.8% |
Source: 1990 U.S. Census data
The West County Toxics Coalition used several strategies in its successful fight against Chevron:
1. Try To Work It Out with the Polluter
The first strategy was to sit down at the table with Chevron. The citizens of Richmond wanted to express their concerns for their health and safety. Rather than choosing an antagonistic strategy, the citizens hoped to cooperate with the corporation for an agreeable solution for all parties involved. Thus, Henry Clark and his cohorts sat down with Mike Hannan, plant manager of the Chevron facilities in Richmond.
Essentially, the members of the West County Toxics Coalition asked for a policy of zero net emissions. The citizens were completely supportive of Chevron's cleaner burning fuel programs, so long as the development of these programs did not endanger their health. They did not want any increased risks to the Richmond community. Therefore, they requested some mitigations from Chevron: the repair of leaking pumps and valves, the shutdown of older parts of the Chevron plant, etc.
Chevron refused to cooperate. This strategy was unsuccessful.
2. Lobby the public officials
What could the citizens of Richmond do next? Chevron refused to listen to their concerns. The local residents thought of an alternative strategy: They would lobby the Planning Commission for the City of Richmond. After all, Chevron needed a land use permit from the city in order to carry out its operations. The residents believed that they had a strong case to present to this Planning Commission with hard scientific data to document the risks to their health and safety from Chevron's operations. Because of this detrimental impact of Chevron's presence in Richmond, the West County Toxics Coalition urged that Chevron must put up 10 percent of the cost of its Clean Fuels Program into a community development fund. This would give citizens of Richmond over $50 million!
The Planning Commission agreed with the citizens. They ordered Chevron to pour $50 million into community development in order to be granted the new land use permit. This strategy was successful because of the power and influence of the community organizing, as well as the hard scientific and legal expertise behind the citizens' efforts. The West County Toxics Coalition had the power of numbers behind them -- mobilizing hundreds of citizens to these Planning Commission boards, and working with the local environmental groups like CBE and the Golden Gate Law Clinic. These were the two other successful parts of the citizens' strategy:
3. Mobilize hundreds of concerned citizens
The West County Toxics Coaltion was able to successfully lobby the Planning Commission in Richmond because it could rally hundreds of committed, impassioned citizens. This is the foundation of any good community organizing effort. The WCTC urged citizens to make phone calls to public officials and make their voices heard. They started letter writing campaigns, demonstrations, and protests, all of which attracted media and turned the tide of public opinion away from Chevron.
4. Find allies with legal and scientific expertise
Too often community groups do not have access to legal power or scientific data that will support their cause. By making allies with so many groups in the San Francisco Bay Area, WCTC was able to overcome these traditional barriers to power. For example, the Golden Gate Law Clinic helped interpret laws like CEQA (the California Environmental Quality Act) to the community's advantage. Scientists at CBE were able to provide the Planning Commission with powerful evidence that the reformulated fuel plan would have detrimental impacts on children and other vulnerable local residents close to the refinery.
The West County Toxics Coalition did an outstanding job of mobilizing the community. It quickly attracted the attention of local media and activists to the nature of the problem. It put pressure on public officials to rule in its favor. Moreover, it scored a great coup in recruiting important allies from the legal and scientific community. All of these were important in the success of the Richmond citizens' efforts.
However, the victory would prove to be short-lived. The citizens of Richmond may have been excellent in resource mobilization with regards to people power, but Chevron had the power of money. Chevron appealed the Planning Commission decision at the City Council, and had the decision overturned. The wealthy corporation argued that the citizens were trying to "extort $50 million" and denied that it had any responsibility to mitigate the problem.
The citizens still won a historic battle (see Solutions below), but it was not as large as anticipated. Chevron did not respect the West County Toxics Coalition and it tried to discredit their efforts altogether. Chevron had a history of giving local politicians large campaign contributions, and it always threatened to leave town if the citizens became too disruptive. So the strategy was weak in its ability to deal with the larger problem of corporate control of City Hall. Perhaps a future strategy for the West County Toxics Coalition would be to mobilize their resources to elect their own local candidates to City Hall. They could take power into their own hands, rather than being dependent on public officials who are beholden to Chevron.
Back to Table of ContentsIn a historic agreement, Chevron agreed to pay up to $5 million to community development projects in Richmond. This money would help fund such important local projects as:
The West County Toxics Coalition had succeeded in getting millions of dollars for the local community. Chevron did not pay the full $50 million that the citizens had initially demanded, but they still had achieved a major breakthrough. Chevron had promised comprehensive economic benefits for members of the fence-line communities. The full details of the project are ennumerated in a Memorandum of Understanding reached on June 2, 1994.
In the aftermath of this agreement, the West County Toxics Coalition has continued to work with local citizens, scientific experts, and legal advocacy organizations to win further concessions from Chevron. In 1996, the citizens managed to shut down a dangerous Chevron incinerator that had been jeopardizing the health and safety of local residents for almost three decades. Working with Greenpeace and local community organizations, the residents of Richmond were able to mobilize enough support to close down the hazardous facility. They sent more than 1500 letters to the California EPA, urging an Environmental Impact Report, plans for immediate closure of the incinerator, and community participation in the project. Two weeks later, Chevron announced it would shut down the incinerator by 1997. The residents of Richmond are currently working in close collaboration with the California EPA to finalize plans for the closure.
Back to Table of ContentsOther communities involved in environmental justice struggles could learn a lot from the successes in Richmond, California. The West County Toxics Coalition has been successful for a number of reasons:
In the future, Richmond residents may find that another good strategy is to take power into their own hands. They may wish to work towards electing a local candidate for City Council, as well as other candidates sympathetic to their cause.They may also choose to increase media attention to their cause. In the progressive circles of the San Francisco Bay Area, they may find many more allies willing to support them, if only people are made aware of the injustices being perpetrated.Finally, they should persist in trying to work in cooperation with Chevron in constructing a common vision for the future of Richmond. It is in the best interests of both Chevron corporation and the residents of Richmond to prevent pollution, reduce toxic emissions, and provide jobs. Citizens of Richmond should continue to sit down at the table with employees of Chevron in order to construct a positive, proactive vision of the future. Rather than fighting each other -- pouring time and resources into costly, energy-draining battles -- they should work together to fight the common problems they share. As Richmond residents have discovered with their victory in the "Clean Fuels" case, Chevron has a lot of power and money that could be used for the good of the community. It's better to have a relationship of goodwill and unity than one of antagonism and division.
Organization: West County Toxics Coalition
Address: 1019 MacDonald Avenue, Richmond, CA 94801
Phone: (510) 232-3427
Fax: (510) 232-4111
E-Mail: n/a
Zero net emissions -- A policy where a company does not increase its release of pollutants into the atmosphere. For instance, Chevron could develop a new form of cleaner burning gas, so long as there are no overall increases in pollution during the process. There should be no increased risk to the community. Hopefully, the corporations can even the emissions of hazardous chemicals coming out of the plants!
Back to Table of ContentsSpecial thanks to Henry Clark and Lucille Allen of the West County Toxics Coalition for their generous help in providing invaluable primary and secondary source material. Thanks also to Anne Simon of the Environmental Law Community Clinic in Berkeley, California.
This page was compiled by Scott Sherman at the University of Michigan. For comments, questions, and other feedback, you may reach me at my e-mail address: scotman@umich.edu