 |
|  |
| |
Carbonic
Anhydrase
|
| |
|
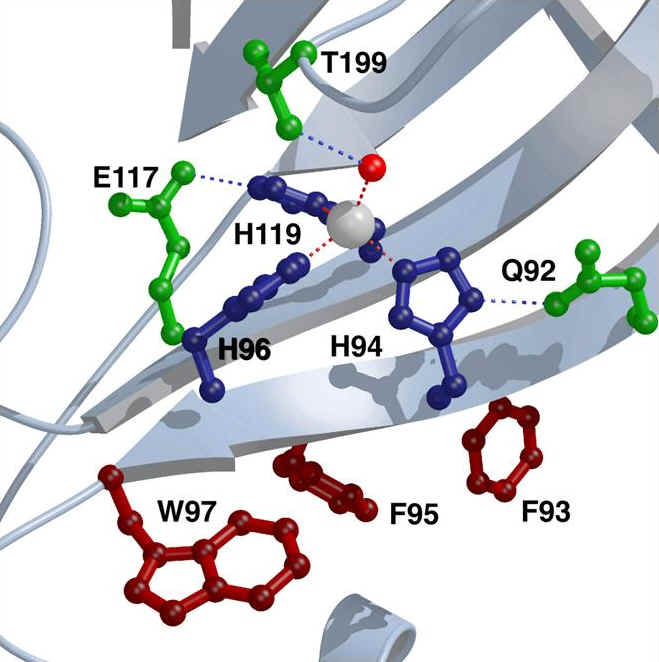
Carbonic anhydrase II (CA) can be
used as the transducer in a biosensor that measures zinc using either
exogenous fluorescent sulfonamides or covalently attached fluorophores.
CA-based sensors with a wide range of zinc affinities (6 orders of magnitude),
kinetics, and specificities have been developed.
The use of CA to measure free metal ion concentrations in
vivo has necessitated further improvements to this sensor. These include
ratiometric sensors that can either be expressed in the cells or introduced
into the cell by a cell importation tag.
|
|
Active site of Carbonic anhydrase
|

|
|
The ratiometric sensors use sulfonamides that bind to the holo-enzyme
by either a covalently attached fluorophore or the DsRed protein fused to the
C-terminus and the FRET donor and acceptor respectively. We are also
continuing to alter the metal specificity by mutating the second shell metal
ligands, and enhancing the protein stability by introducing a disulfide bond
to further optimize CA-based biosensors for the measurement of zinc and copper
ions in both in
vitro
and in
vivo conditions.
PubMed
Search
Collaborators on this project:
Richard Thompson |
|
 |