Correlation Table

No spectrum provided by supplemental info packet
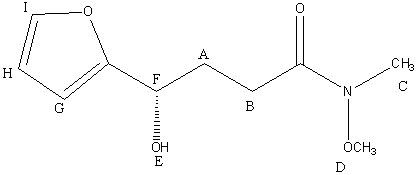
Molecule 24
A; 2.05 (multiplet, 2H); these Hs are attached to an sp3 carbon that are both in the vicinity of oxygens, which cause the Hs to be more downfield shifted than a regular sp3 CH2 peak. Also, it is a multiplet because of the many bond neighbors on the two neighboring carbons.
B; 2.10 (multiplet, 2H); these Hs are attached to an sp3 carbon and it is in the vicinity of a C = O, which causes the Hs to be shifted more downfield. Also, there are many different bond neighbors, causing the peak to be a multiplet.
C; 2.71 (s, 3H); these Hs are on an sp3 carbon that is attached to a nitrogen, causing the peak to be more downfield-shifted than a normal CH3 peak. There are no bond neighbors.
D; 3.67 (s, 3H); these Hs are on an sp3 carbon that is attached to an oxygen, causing the peak to be far more downfield-shifted than a regular CH3 peak.
E; 3.69 (br, 1H); this H is directly attached to an oxygen, causing it to be strongly downfield-shifted and causing the peak to be broader than a normal C-H peak.
F; 4.74 (t, 1H); this H is very downfield shifted because it is connected to a carbon that is connected to an alcohol group. The carbon is also connected to an aromatic furan ring, causing the H to be even more deshielded. Also, it is a triplet because its neighboring CH2 has two diastereotopic Hs.
G; 6.39 (d, 1H); this H is on an aromatic furan ring, causing it to be strongly downfield-shifted due to all the polarity and resonance caused by the aromaticity of the ring. Furthermore, there is an oxygen in the ring, which also contributes to the shift.
H; 6.47 (dd, 1H); this H is on an aromatic furan ring, causing it to be very downfield-shifted. It is a doublet of doublets because of the bond neighbors in the ring.
I; 7.67 (d, 1H); this H is on an aromatic furan ring and it is attached to the carbon that is attached to the oxygen that is in the ring, which all contribute to the strong downfield shift of this H.