Experimental
In a flame dried round bottom flask molecule 18 (368 mg, 0.686 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (DCM) (6.9 mL, 0.1 M) and cooled to -78°C. DIBAL was added dropwise (1M solution in hexanes, 2.4 mL, 2.4mmol, 3.5 eq) to the flask and stirred for 30 minutes at -78°C. Methanol (CH3OH) (0.25 mL) was used to quench the solution and the solution was warmed to room temperature. Ethyl acetate was added to dilute the solution. Hydrochloric acid (HCL) (3M, 15 mL) was added and the biphasic mixture was stirred vigorously for 15 minutes. The layers were separated and the aqueous layer was exhaustively extracted with ethyl acetate (4 x 5 mL). The organic layer was washed with brine (10 mL), dried with sodium sulfate (MgSO4), and concentrated to give the crude product. The crude product of Molecule 19 was obtained as an orange/red foam and carried onto the next step without purification, quickly in order to prevent decomposition. In order to purify Molecule 19, the crude product was dissolved in DCM and extracted exhaustively with 10% aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The combined base washes were then acidified and back extracted with ethyl acetate. The purified Molecule 19 (63% yield isolated on 35 mg scale) was obtained as a light yellow foam.
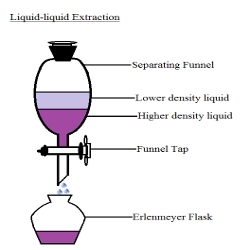
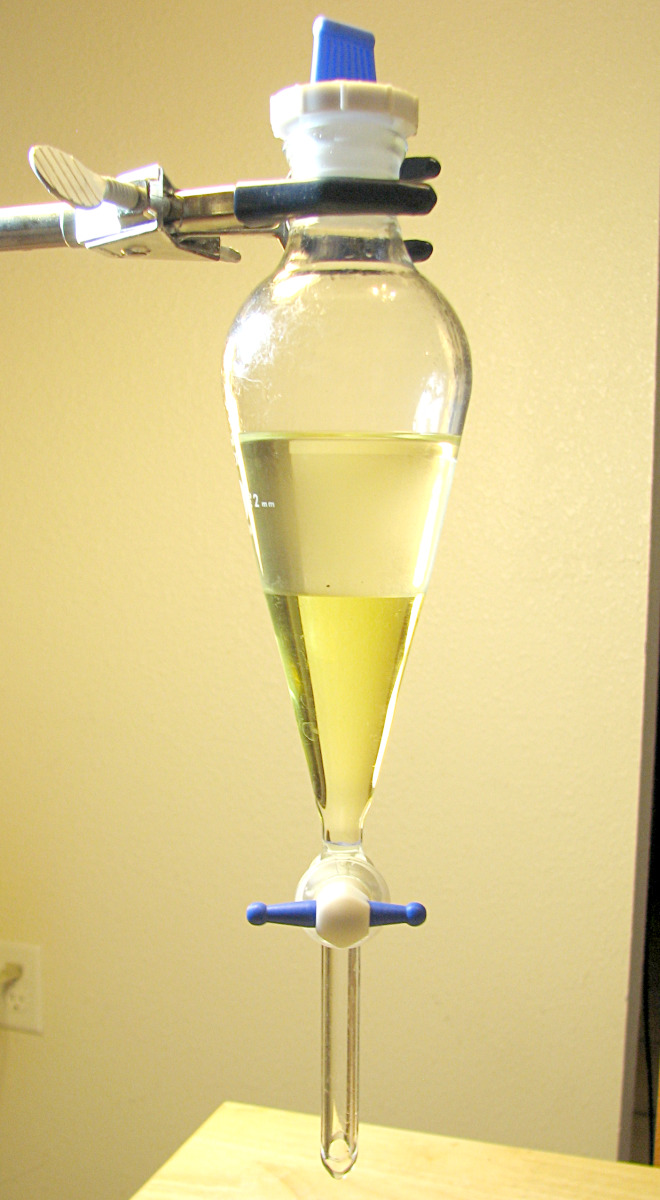
Liquid-Liquid Extraction
A method used to separate two immiscible phases of liquid from each other. Usually, a non organic layer is separated from an organic layer with the use of a separatory funnel and different solvents. In this experiment, the aqueous and organic layers are being separated with the help of ethyl acetate.
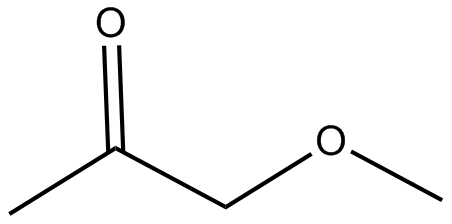
Purified Molecule 19 Product (63% yield isolated on 35 mg scale): Rf = 0.76 (silica gel, EtOAc); HRMS (m/z): calcd for C22H18O7, [M-H]-, 393.0980; found, 393.0976; IR (film) νmax: br 2923, 1702, 1503, 1490, 1250, 1035, 929 cm-1;1H NMR (400MHz, CDCl3): δ 9.85 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1 H), 6.91 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1 H), 6.81 – 6.72 (m, 5 H), 6.46 (dd, J = 15.7, 0.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.12 (dd, J = 15.8, 6.9 Hz, 1 H), 5.95 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 4 H), 3.83 (t, J = 9.6 Hz, 1 H), 3.51 – 3.38 (m, 1 H), 3.23 – 3.04 (m, 2 H) ppm; 13C NMR(CDCl3, 101 MHz): δ 200.3, 178.3, 148.2, 148.1, 147.6, 146.9, 134.3, 131.6, 130.8, 126.7, 121.4, 119.9, 108.5, 108.4, 107.3, 105.7, 101.3, 101.2, 55.6, 48.3, 40.7, 39.7 ppm.

Molecule 19
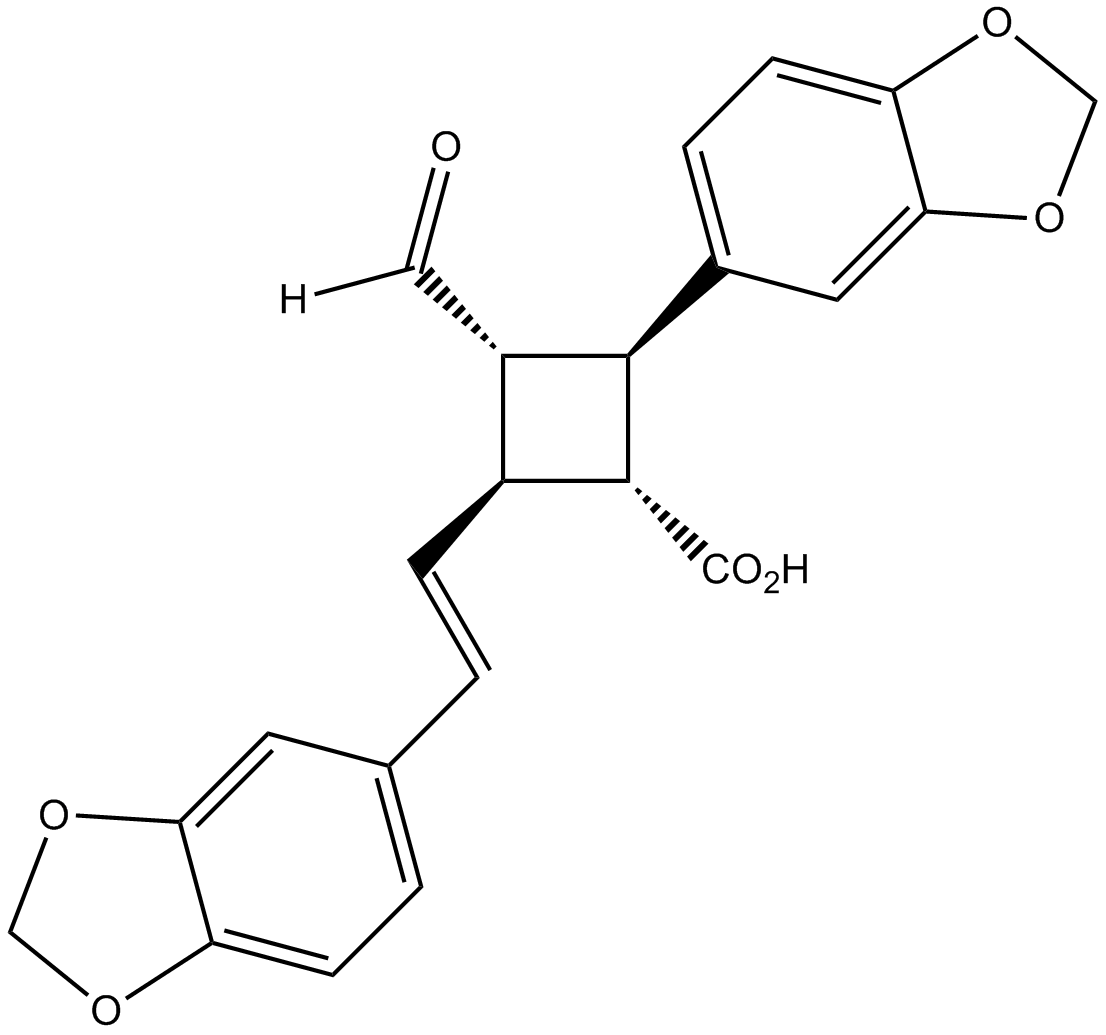
The product of the reaction!
Back Extraction
To turn the extracted phase back into its original phase. For example in this experiment, ethyl acetate was put back into the organic layer in order to extract the aqueous layer out again.
Sodium Hyroxide
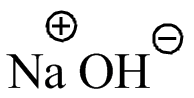
Sodium Sulfate
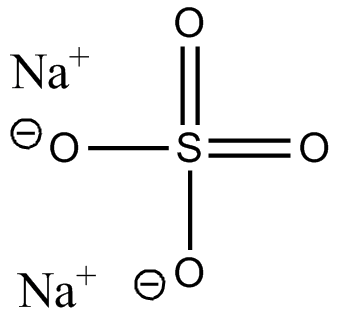
Sodium sulfate reacts with water to remove it from organic layer
Biphasic Mixture
A solution made up of two immiscible phases. In this experiment, the two phases are the organic and aqueous layers.

Hydrochloric Acid ![]() Hydrochloric Acid is used to protonate molecules and help seperate compounds from byproduct.
Hydrochloric Acid is used to protonate molecules and help seperate compounds from byproduct.
Hydrochloric Acid is used to protonate molecules and help seperate compounds from byproduct.
Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl Acetate is used to create the biphasic mixture. It evaporates easily at room temperature and has a high boiling point, thus making it's ideal for seperation of products.
Quenching
A method of work up used to deactivate any non-reacting reagents. In this experiment, methanol is being use to deactivate the reagents that are not reacting in the reaction.
Methanol
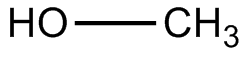
Methanol is used to quech the reaction, or deactivate the non-reacting reagents.
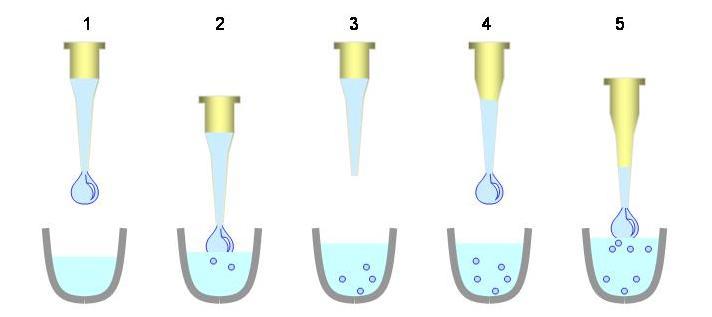
Dropwise
A method of adding one solution to another "drop" by "drop". This process occurs slowly, and its purpose is usually to prevent violent reactions from occurring. This technique can be done by an addition funnel, pipette, or some type of needle. In this experiment, DIBAL is being added dropwise.
DIBAL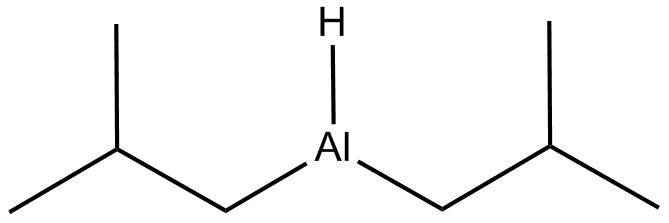
DIBAL is used to convert the amide in Molecule 18 to the aldehyde in molecule 19.
Dicholoromethane (DCM)
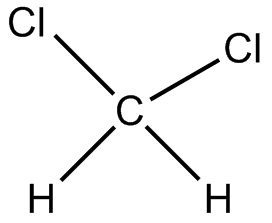
DCM is used as a solvent and is miscible with many organic solvents, but not misible with water.
Molecule 18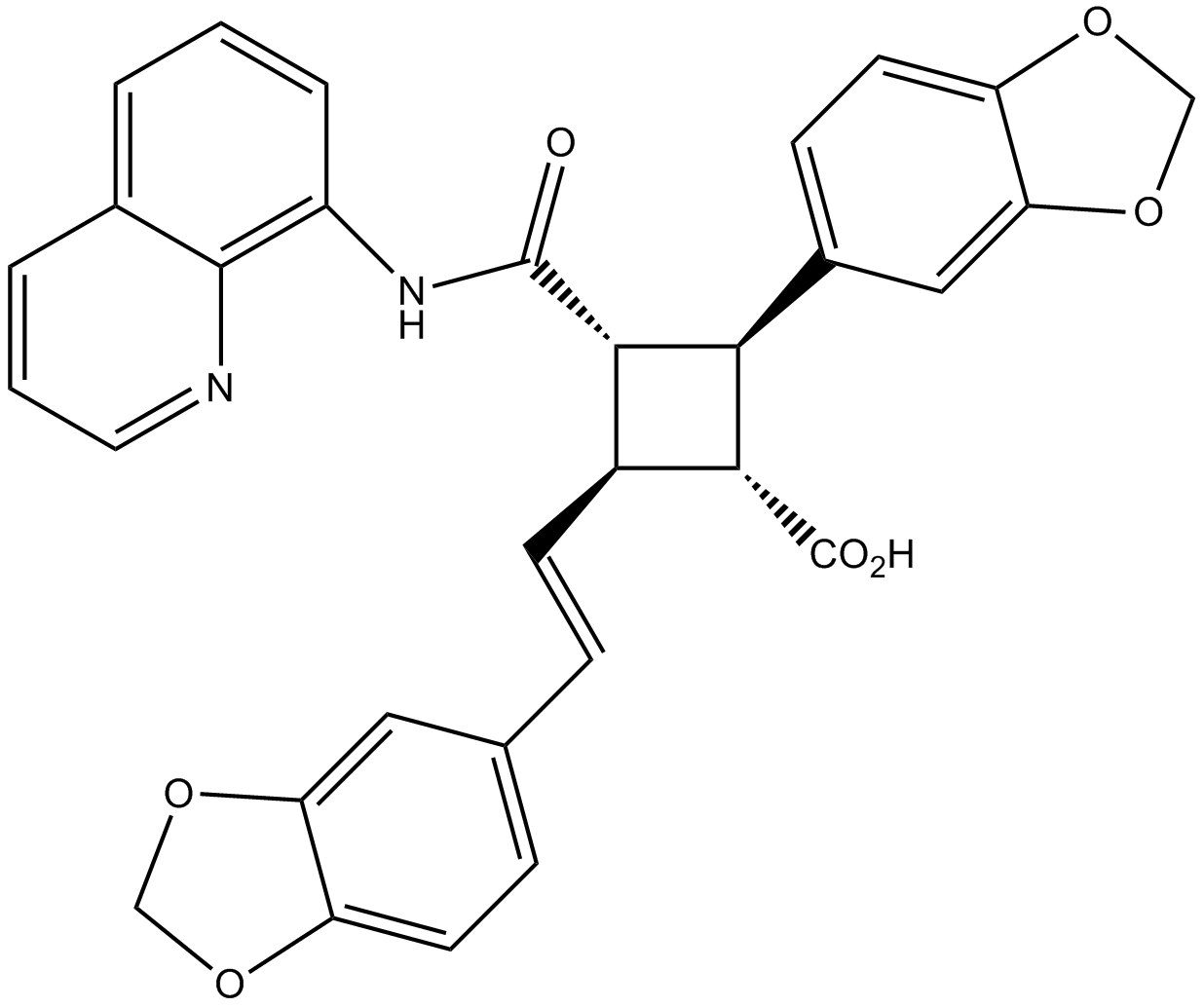
The Starting Material/Product
