

Leading Question
How does the biological activity of cortistatin A(1) compare to that of cortistatinone(8)?
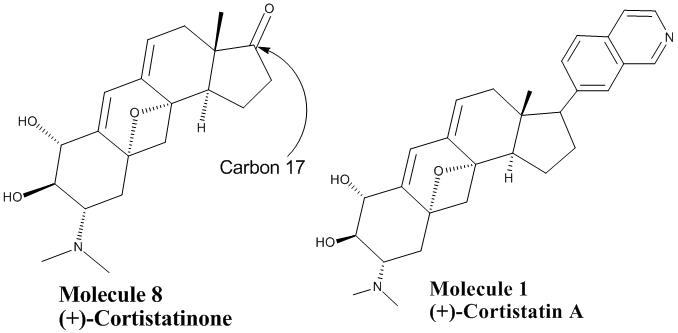
Cortistatin A is a powerful inhibitor of HUVAC protein responsible for angiogenesis (growth of blood vessels) found in cancers and obesity. It is a member of a family of steroids known collectively as cortistatins. All of these cortistatins have similar biological activity, however cortistatin A is the most deadly to the angiogenic cells and causes the fewest unwanted collateral effects. Cortistatinone, from which Baran and colleagues synthesized cortistatin A, differs from cortistatin only in the functional group at carbon 17. Cortistatin has an isoquinoline group whereas cortistatinone has a carbonyl. The isoquinoline group is highly biologically active. It is present in some anaesthetics, anti-hypertension agents, anti-fungal compounds, vasodialators, and neuroroxins and is found in many of the cortistatin family steroids. All cortistatins share some nitrogen-containing group at carbon 17 and all have some biological activity, and thus it can be assumed that at least part of their biological activity can be attributed to this group. Since cortistatinone lacks this nitrogen-containing group we suspect that its biological activity will be different, and probably not beneficial. The carbonyl group is more reactive than the isoquinoline, so cortistatinone may have diverse and non-specific reactions in the body.
Leading Question

|
|