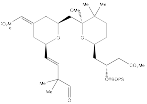
Aldehyde 15 to Compound 3
Step 1: Aldehyde 15 was dissolved with distilled MeOH (1.5 mL). Ohira-Bestmann reagent (55.6 mg, .289 mmol) and K2CO3 (60 mg, .435 mmol) were added to above solution at 0 °C. This mixture was stirred for 1 h, before it was poured into a pH 7.0 buffer. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and the combined organic fractions were dried over Na2SO4. The terminal acetylene was purified via silica gel flash column chromatography (10%, then 15% ethyl acetate/ petroleum ether) to give a colorless oil (125 mg, 97%).
Step 2: TBAF (I M buffered with 20 mol % HOAc in THF, .24 mL) was added to a solution of the above terminal acetylene (193 mg, .216 mmol) in THF (4.0 mL) at rt under N2. The resulting red solution was stirred at rt for 10 h, before it was poured into a pH 7.0 buffer. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and the combined organic fractions were dried over Na2CO4. Compound 3 was purified via silica gel flash column chromatography (15%, 30% then 10% ethyl acetate/petroleum ether) to give a colorless oil (127 mg, 90%, brsm 96%, 13 mg starting material was recovered). Rf: .35 (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether, 2:3 v/v); [a]D20(deg cm3 g-1 dm-1): +65.7 (c 0.16 g cm-3 in DCM); IR (film): 3292 (br), 2950, 2858, 1739, 1718, 1651, 1513, 1435, 1247, 1110, 705 cm-1
Glossary
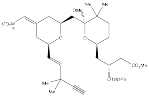
Aldehyde 15:
Reacts with the Ohira-Bestmann reagent to produce the terminal acetylene.
DCM: Methylene Chloride (CH2Cl2); solvent.
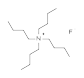
TBAF (tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride):
Used as a deprotecting reagent with silyl ether protecting groups (in this case the group TBDPS).
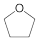
THF (tetrahydrofuran):
Polar, aprotic solvent.
HOAc (Acetic Acid.
Buffer.
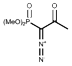
Ohira-Bestmann reagent:
The Ohira-Bestmann reagent (also known as dimethyl (1-diazo-2-oxopropyl) phosphonate) is the Ohira-Bestmann modification of the Seyferth-Gilbert Homologation, allowing enolizable aldehydes to be transformed into alkynes under relatively mild reaction conditions.
“Rt”: room temperature.
Terminal acetylene:
Reacts with TBAF to form Compound 3 (deprotection reaction).
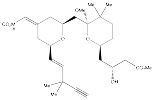
Compound 3:
Formed from the two-step synthesis described.
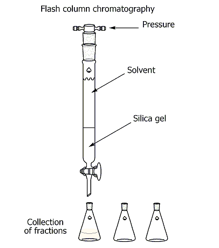
Flash column chromatography:
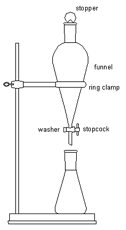
A method used to purify individual chemical compounds from mixtures of compounds, which could not be otherwise separated. Typically, a column consists of lightly packed glass wool, a smooth layer of sand, a layer of silica gel, another layer of sand, and eluent (in this case mixtures of petroleum ether/ ethyl acetate). The sample is deposited onto the sand, and allowed to travel through the column. Flash column chromatography refers to when compressed gas, such as Nitrogen or air, or a pump is used to increase the rate of flow of the eluent (decreasing the amount of time it takes for the sample to pass through the column and separate).
pH 7.0 buffer:
A buffer solution is an aqueous mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The pH of the solution changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used to keep pH at a nearly constant value in a number of chemical applications.
Extraction (liquid-liquid):
Liquid-liquid extraction, also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, typically water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid phase into another. Liquid-liquid extraction is performed using a separatory funnel. It is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.